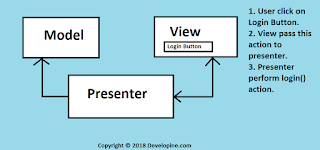
In this example I will show you how to get precise call state in Android programatically using java reflection API.
Add this in Android Manifest file. Declare Broadcast receiver.
<receiver
android:name=".OutCallLogger"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.PRECISE_CALL_STATE" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.NEW_OUTGOING_CALL" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>Add below permissions in android manifest file.<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.PROCESS_OUTGOING_CALLS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PRECISE_PHONE_STATE" />
Also add this line in manifest file. <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.telephony"></uses-feature>And this is your class which will be used for getting precised call state for outgoing calls. public class OutCallLogger extends BroadcastReceiver {public OutCallLogger() {
}
TelephonyManager Tm;
ITelephony telephonyService;
Class c = null;
Method methodGetInstance = null;
Method methodGetActiveFgCallState=null;
String TAG="Tag";
Object objectCallManager=null;
Context context1;
Class<?> classCallManager;
Class telephonyClass;
Class telephonyStubClass;
Class serviceManagerClass;
Class serviceManagerStubClass;
Class serviceManagerNativeClass;
Class serviceManagerNativeStubClass;
Method telephonyCall;
Method telephonyEndCall;
Method telephonyAnswerCall;
Method getDefault;
Method[] temps;
Constructor[] serviceManagerConstructor;
// Method getService;
Object telephonyObject;
Object serviceManagerObject;
private Timer timer= null;
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
// TODO: This method is called when the BroadcastReceiver is receiving
// an Intent broadcast.
this.context1= context;
Tm=(TelephonyManager)context.getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);final ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
try {
classCallManager = classLoader.loadClass("com.android.internal.telephony.CallManager");
Log.e(TAG, "CallManager: Class loaded " + classCallManager.toString());
methodGetInstance = classCallManager.getDeclaredMethod("getInstance");
methodGetInstance.setAccessible(true);
Log.e(TAG, "CallManager: Method loaded " + methodGetInstance.getName());
objectCallManager = methodGetInstance.invoke(null);
Log.e(TAG, "CallManager: Object loaded " + objectCallManager.getClass().getName());
Method[] aClassMethods = classCallManager.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : aClassMethods)
{
Log.e("MEthods", m.getName());
}
methodGetActiveFgCallState = classCallManager.getDeclaredMethod("getActiveFgCallState");
Log.e(TAG, "CallManager: Method loaded " + methodGetActiveFgCallState.getName());
Log.e(TAG, "CallManager: What is the Call state = " + methodGetActiveFgCallState.invoke(objectCallManager));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getClass().getName() + e.toString());
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getClass().getName() + e.toString());
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getClass().getName() + e.toString());
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getClass().getName() + e.toString());
}
Tm.listen(new PhoneStateListener(){
public void onCallStateChanged(int state,String number) {
super.onCallStateChanged(state, number);
try {
if (methodGetActiveFgCallState.invoke(objectCallManager).toString().toLowerCase() .equals("idle"))
{
//Toast.makeText(context1, "I am in idle state", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); }
if (methodGetActiveFgCallState.invoke(objectCallManager).toString().toLowerCase() .equals("active"))
{
//Toast.makeText(context1, "I am in active state", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); }
Toast.makeText(context1, " "+methodGetActiveFgCallState.invoke(objectCallManager).toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CALL_STATE);
}
A Toast will appear which will tell you about call state. Find a line which shows Toast.